 Image 1 of 1
Image 1 of 1


Chip Research Quote
Chip Decryption
Chip decryption refers to the technical process of analyzing and interpreting encrypted information stored within an integrated circuit. This may involve advanced examination of the chip’s architecture, security protocols, and data structures to understand its internal programs or protected data. Such work is typically conducted within a legal and ethical framework, for purposes such as security evaluation, interoperability, legacy system support, or academic research.
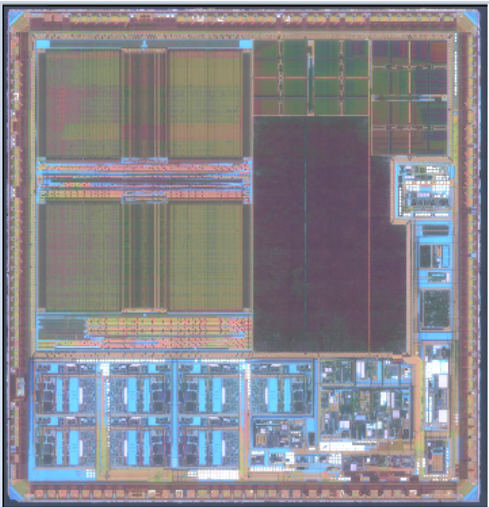
Chip Reverse Engineering
Chip reverse engineering refers to the systematic analysis of existing semiconductor products to understand their functional principles, design architecture, and implementation methods. This process may involve examining the chip’s circuitry, layout, and operation in order to gain technical insights. When conducted responsibly, reverse engineering can support legitimate purposes such as product interoperability, academic research, design verification, failure analysis, and the development of compatible technologies.
Chip ROM Program Extraction
ROM (Read-Only Memory) commonly contains the firmware or operating system that governs a chip’s functionality. Program extraction refers to the technical process of accessing and retrieving firmware data stored in ROM by means of specialized hardware interfaces and software tools. When performed appropriately, ROM program extraction can serve legitimate purposes such as legacy system support, security analysis, academic study, or design verification.
Encrypted Chip Analysis
Encrypted chip analysis is a specialized area of reverse engineering that focuses on studying and evaluating the security mechanisms and encryption architectures used in protected chips. This process involves examining how encryption is implemented in order to better understand system resilience, verify design integrity, and assess potential vulnerabilities. Such analysis, when conducted within lawful and ethical boundaries, supports important applications including security research, interoperability, compliance testing, and academic study.
Chip Encryption
Chip encryption refers to the integration of security mechanisms within semiconductor design to safeguard embedded programs and data against unauthorized access, duplication, or tampering. These protections are typically implemented through a combination of hardware features, firmware controls, and advanced cryptographic algorithms, forming a critical component of modern chip security architecture.
Model Identification
Model identification refers to the process of determining the specific type, version, and technical specifications of a chip. This may involve examining its physical attributes, electrical characteristics, or embedded program structures. Accurate model identification is essential for understanding a chip’s compatibility, functionality, and performance, and it supports legitimate applications such as maintenance, system integration, design verification, and reverse engineering.
Chip Decryption
Chip decryption refers to the technical process of analyzing and interpreting encrypted information stored within an integrated circuit. This may involve advanced examination of the chip’s architecture, security protocols, and data structures to understand its internal programs or protected data. Such work is typically conducted within a legal and ethical framework, for purposes such as security evaluation, interoperability, legacy system support, or academic research.
Chip Reverse Engineering
Chip reverse engineering refers to the systematic analysis of existing semiconductor products to understand their functional principles, design architecture, and implementation methods. This process may involve examining the chip’s circuitry, layout, and operation in order to gain technical insights. When conducted responsibly, reverse engineering can support legitimate purposes such as product interoperability, academic research, design verification, failure analysis, and the development of compatible technologies.
Chip ROM Program Extraction
ROM (Read-Only Memory) commonly contains the firmware or operating system that governs a chip’s functionality. Program extraction refers to the technical process of accessing and retrieving firmware data stored in ROM by means of specialized hardware interfaces and software tools. When performed appropriately, ROM program extraction can serve legitimate purposes such as legacy system support, security analysis, academic study, or design verification.
Encrypted Chip Analysis
Encrypted chip analysis is a specialized area of reverse engineering that focuses on studying and evaluating the security mechanisms and encryption architectures used in protected chips. This process involves examining how encryption is implemented in order to better understand system resilience, verify design integrity, and assess potential vulnerabilities. Such analysis, when conducted within lawful and ethical boundaries, supports important applications including security research, interoperability, compliance testing, and academic study.
Chip Encryption
Chip encryption refers to the integration of security mechanisms within semiconductor design to safeguard embedded programs and data against unauthorized access, duplication, or tampering. These protections are typically implemented through a combination of hardware features, firmware controls, and advanced cryptographic algorithms, forming a critical component of modern chip security architecture.
Model Identification
Model identification refers to the process of determining the specific type, version, and technical specifications of a chip. This may involve examining its physical attributes, electrical characteristics, or embedded program structures. Accurate model identification is essential for understanding a chip’s compatibility, functionality, and performance, and it supports legitimate applications such as maintenance, system integration, design verification, and reverse engineering.